When is Cellulitis an Emergency?
Cellulitis: What you Need to know and When to Visit the ER
Cellulitis is a skin disease, a bacterial skin infection of the skin and soft tissues. Cellulitis is usually caused by staphylococci (“staph”) or streptococci (“strep”) bacteria that live on the skin or inner surface of the nose or mouth.
Cellulitis emergency happens when bacteria manages to get under the skin and spread to the tissues beneath, cellulitis can develop. The bacteria responsible are Streptococcus or Staphylococcus.
In most cases, Cellulitis Emergency is not a serious, life-threatening infections disease, and as a bacterial skin infection, is easily treated with antibiotics. Cellulitis Emergency does, however, need treating, since if you leave it to its own devices it will probably get worse.
If you suspect a cellulitis emergency you should go and see your doctor as soon as possible to avoid potential complications. Keep an eye on the affected area from day to day as it can spread rapidly, and if you notice any worsening or spreading of the cellulitus signs or symptoms, seek medical care.
What Does Cellulitis Emergency Look like?
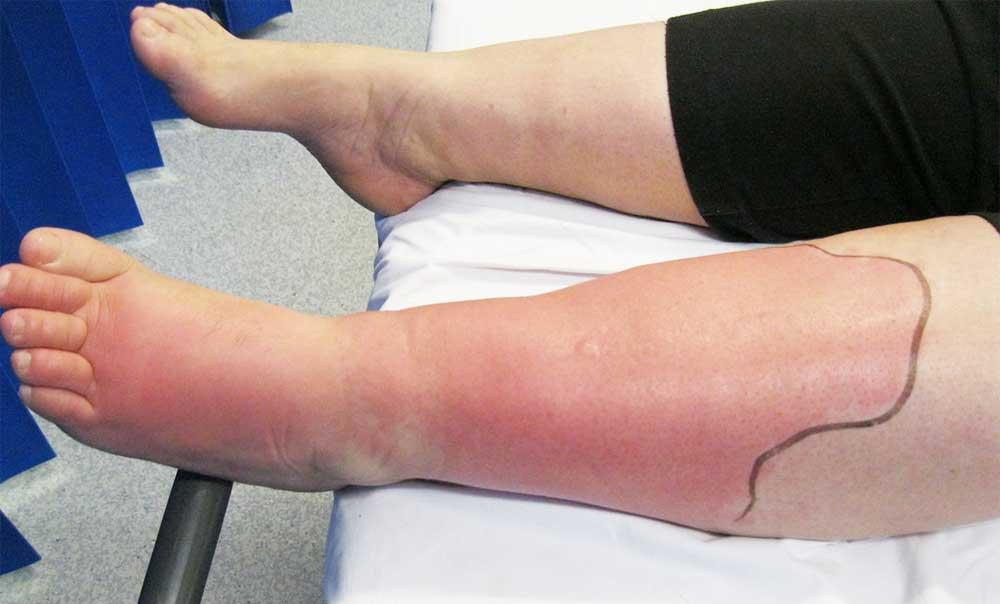
The first thing you may notice is redness and inflammation at the site of the infection. This may swell, feel warmer to the touch and surrounding areas, and become painfully tender. The skin may crack or split and leak fluid or pus and you may notice red streaks extending from the area.
As well as these physical symptoms you may have a general feeling of illness or malaise. In more severe instances you may also experience fevers, chills, and sweats.
What Causes Cellulitis?
Cellulitis can occur to anyone, and anyone can be at risk from cellulitis emergency. It can affect almost any part of the body, especially where the skin is damaged or broken.
- Broken or damaged skin can come from skin conditions such as eczema, acne, psoriasis or scabies as well as from general cuts and grazes.
- Insect bites puncture the skin causing break in the skin, and can put you at risk.
- Cellulitis can sometimes result from surgical wounds.
- Foreign objects becoming embedded in or under the skin (such as glass, metal or ceramics) can lead to cellulitis.
Cellulitis Diagnosis
Cellulitis emergency diagnosis is normally a simple matter for your doctor, based on a physical exam and your medical history.
Occasionally the doctor may request some blood work or blood tests if he or she suspects infection has passed into the bloodstream, or to check your white blood cell count. If a foreign object is suspected, the doctor may also order an x-ray. In some instances, fluid may be taken from the affected area then sent to the lab for testing.
See also: Psoriasis : Challenges, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cellulitis Treatment
Cellulitis emergency is normally treated with antibiotics you can take orally for a week to ten days. If antibiotics are prescribed for you, make sure you take the entire course of treatment even if the infection seems to be getting better after a few days. In rare cases stronger antibiotics may be needed and these are generally given in hospital intravenously (although sometimes this can be administered at home).
During your recovery at home, you should get plenty of rest so the body can concentrate on fighting the infection. If you can keep the area of infection raised, this will help ease swelling, improve drainage and reduce any pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also help reduce inflammation or fevers.
Preventing Cellulitis Emergency
Sensible precautions against accidental injuries are the first guard against cellulitis. For instance, taking care when using knives or other sharp instruments, and not going barefoot in hazardous areas such as on the beach or in the forest.Cellulitis is also easily spread from skin to skin contact or by touching infected surfaces.
Simple precautions can help reduce the chances of infection spreading:
- Daily showering or bathing.
- Frequent hand washing.
- Keeping wounds covered.
- Not sharing towels with others.
- Regularly changing and washing bed linen.
When Cellulitis Becomes an Emergency
There are some instances when cellulitis needs urgent emergency room treatment. If you notice any of the following symptoms, please treat them seriously and get urgent medical care:
- The red or tender area going numb
- The reddened area becoming larger or hardening
- A blackened area that feels tender, warm and swollen
- Pain gets worse
- Vomiting or nausea
- High fevers or chills
Certain pre-existing medical conditions can also increase the seriousness of cellulitis, so if you have any of the following you should also seek urgent medical care:
- Diabetes
- Liver conditions such as cirrhosis or hepatitis
- Kidney disease
- Circulatory problems or varicose veins
- Eczema or psoriasis
- Any medical problems that can be made worse by other infections
- Impaired immune systems
In addition, certain areas of the body are more sensitive than others, for instance in or around the eyes. Children with facial cellulitis can sometimes develop brain or eye infections. These are potentially dangerous so should always be treated as an emergency.
Often, skin conditions don’t appear to be an emergency initially, but in the long term, they can become problematic. As with any health concern, prompt treatment results in faster healing and fewer complications. It is far better to seek medical advice as soon as you suspect infection rather than waiting to see what happens.




