Common Allergens that Trigger Eczema Flares
While it is still not possible to cure eczema or prevent a flare, it is possible to manage the condition and reduce the number of uncomfortable red, rashy outbreaks. Research suggests that those living with eczema tend to have an overactive immune system response when substances, either inside or outside of the body, trigger an alert within the system.
Many people with eczema also have a history of allergies, like hay fever, asthma, or food allergies. Those who do not have allergies at the time their eczema surfaces have a 40 percent higher risk of developing allergic conditions later in life. When food allergies are suspected of causing skin reactions, the removal of suspected foods could improve skin symptoms.
Recognizing Eczema Symptoms
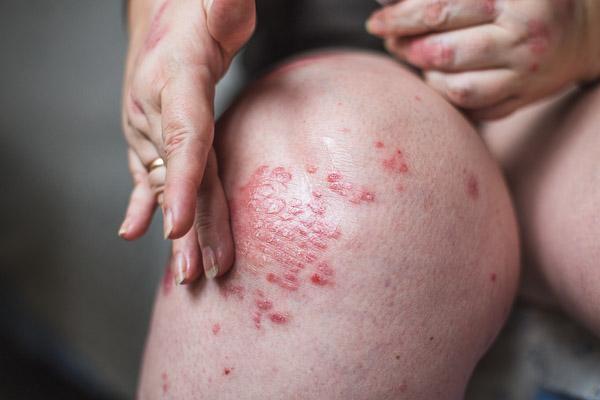
Eczema is typically characterized by an itchy, red rash. An eczema rash can appear scaly or resemble chicken pox. Most often an eczema rash will appear at the elbow, the back of the neck, or on the cheeks, but it can appear anywhere on the body, particularly in infants. While some children outgrow the condition by their teen years, eczema can develop at any time and flares can continue through life. Some of the symptoms of allergic eczema include:
- Skin itching and inflammation
- Red bumps that may drain, ooze or crust
- Warm tender skin
- Dry, rough or red skin
- Dark, thickened skin when rashes subside
Eczema Triggered by Food Allergies
If you suspect that eczema is triggered by a food allergy, it may be best to consult with your physician and discuss the possibility of allergy testing. Knowing what foods to avoid may spare you or your child a potentially serious allergic reaction. But it is possible for foods to trigger eczema without any other life-threatening symptoms. Some common sources of foods that can trigger eczema include:

- Cow’s milk
- Soya
- Eggs
- Fish
- Wheat
- Nuts
Symptoms of food induce allergic reactions may appear anywhere on the body, but may also create a noticeable rash or irritation around the mouth.
Eczema Triggered by Skin Contact
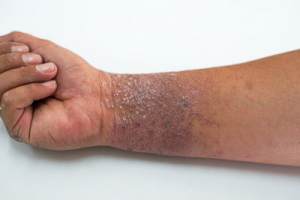
While some eczema flares are triggered by allergic reactions to food sources, skin contact with an irritant can also cause an outbreak. Research shows that many people living with eczema have a specific gene mutation that causes a decrease in the production of filaggrin, a protein that helps maintain a protective healing barrier on the skins surface. This mutation may explain why those with eczema have dry, easily infected skin that is often sensitive to contact with potential irritants.
See Also: How to Tell if Your Child Has Asthma or Allergies – When to Visit the Emergency Room.
Typically, an allergic eczema outbreak will clear within two to three weeks after exposure to the allergen. Once the culprit is identified, you can take steps to avoid repeat exposure. Some of the more common allergic eczema triggers include:
- Nickel allergies -avoid products containing nickel, including jewelry coins, eyeglass frames, cooking equipment and eating utensils
- Latex – avoid exposure from balloons, toys, bandages, shoe soles, baby bottle nipples, and foods prepared while wearing latex gloves
- Chemical reactions to sunscreens – chemical sunscreens react with sunlight. Try using a mineral based sunscreen product
- Soaps and cleaning products – use a soap-free cleanser and natural cleaning products to replace harsh chemicals
- Chlorinated swimming pools – using a rich moisturizer prior to exposure may help prevent a reaction
- Fragrances -avoid products with added fragrance, a common allergen due to the many unlisted chemicals
- Fabrics such as wool or polyester – avoid suspect fabrics in favor of natural fibers like cotton or silk
- Cocamidopropyl betaine used to thicken shampoos and lotions – pay attention to your product labels to avoid this potential allergen
- Dust mites-protect mattresses and pillows with dust-proof mattress and pillow covers and consider eliminating carpets where mites can thrive
- Pet dander-weekly pet bathing can reduce the amount of dander in your environment. Also, consider removing carpeting and investing in an air cleaning system if you decide to keep the pet
If you notice a reaction after contact with a suspected allergic trigger, it’s recommended to wash the area with water to remove any traces of the skin irritant. Then apply a rich moisturizing product to keep skin hydrated and prevent further skin damage.




