Written by Dr. Ruby Rose, MD.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), or “Heartburn”, has likely affected you at some point in your life. Up to 20% of people suffer from symptoms or heartburn or GERD at least once a week.
This is the body’s way of telling you you’re eating something it doesn’t like or can’t process.
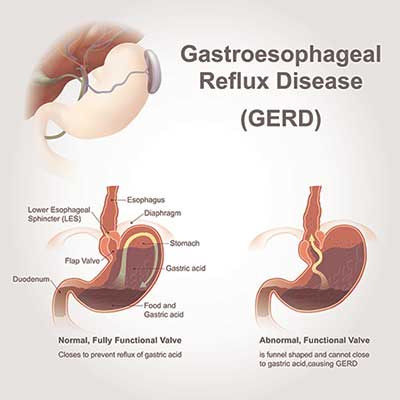
GERD occurs when gastric contents and acid abnormally enter the esophagus causing a myriad of symptoms including retrosternal burning, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, laryngitis, cough, and dysphagia (painful swallowing). This can eventually lead to esophagitis, strictures, Barrett’s esophagus, and cancer.
Causes of GERD
Some of the causes of GERD include lower esophageal sphincter (LES) relaxation, increased intra-abdominal pressure (obesity, pregnancy, hiatal hernia, ascites, tight clothes, recumbent position), stress, decreased saliva, toxins and medications.
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is a condition that results from damage to the GI mucosa and affects the stomach and duodenum. Patients complain of bloating, nausea, early satiety, altered bowel habits and heartburn but some may have no complaints. PUD can lead to GI bleeding, perforation, and peritonitis. Factors that affect the GI mucosal integrity include internal disorders (immune disorders, poor wound healing, vitamin deficiencies) and external insults (H. Pylori, NSAIDs, poor diet, food allergies).
H.pylori is a bacterium that increases the incidence of PUD by 4 times by damaging the protective effects of the gastric mucosa. It has been linked to gastric cancer, B12 and iron deficiency, and ITP.
Traditional Therapy with Pharmaceuticals
H2 blockers and PPIs
Although effective (PPIs>H2B)- chronic use causes acid suppression which can lead to:
- Decreased Iron, B12, magnesium, protein, calcium absorption
- Increased gastroenteritis and pneumonia in kids and adults
- Increased community acquired C-Diff
- Increased gastric carcinogens
- Increased hip and spine fractures
Alternative Approaches: Botanical Options
Demulcent: Mucilaginous or gelatinous substance that soothes, cools and protects irritated or inflamed internal tissues. Acts topically and is not digested by the human body.
1. Licorice
Licorice has many uses due to its anti-inflammatory effects and is used extensively in compounds aimed at the gut. This is my go-to botanical for acid reflux symptoms. We also use it for weaning patients off steroids and PPIs.
Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice (DGL):
- This topical form of licorice avoids the pseudoaldosteronism effects of the phytochemical glycyrrhizin which can cause low potassium, HTN, edema, high sodium.
- DGL extract comes in 380mg chewable tabs and can take 2-4 tabs, 3 times a day as needed, prior to meals or if you have heartburn.
- DGL is safe for the majority of patients including children and pregnancy. DGL also comes in a mouthwash and capsules from which the powder can be dissolved into a paste and you can swish and spit for oral ulcers, canker sores, sore throat, and cough. Can also use topically for herpes, eczema and psoriasis.
- If using the pure form of licorice (NOT DGL), you can take up to 3g/d of root (up to 600mg glycyrrhizin) for less than 6 weeks. This is not recommended for patients with HTN, coronary artery disease, liver/kidney disease, pregnancy, diabetes or if taking blood thinners or on chemo agents.
See also: When is Cellulitis an Emergency?
Other uses for Licorice:
- Antiviral effects against Flu A, Herpes, Zoster, and HIV and local antimicrobial effects (H.Pylori).
- Menopausal hot flashes, elevated liver enzymes associated with NAFLD (non alcoholic fatty liver disease).
- uUsed topically with aphthous ulcers and atopic dermatitis.
2. Slippery Elm:
- Helpful for gastritis, enteritis, colitis, and diarrhea. It can also be used topically on abscesses, hemorrhoids and burns.
- 1tsp Root bark powder can be mixed with 1c cold water, let sit for 10 min. Add to hot water or cereal. Can be sweetened with cinnamon, honey, maple syrup or stevia.
- Do not take concurrently with other meds due to binding.
- Minimal side effects and safe in children and pregnancy.
3. Marshmallow Root:
- Mucilaginous herb used for pharyngitis, wound healing, bronchitis, constipation.
- Safe in children. May absorb meds taken concurrently.
4. German Chamomile:
- Anti-spasmotic and anti-inflammatory for the GI tract. The flower actually contains compounds that promote mucosal prostaglandin production (which is what is suppressed when you take NSAIDs) and smooth muscle relaxation of the stomach and duodenum. Used in IBS and colitis.
- Used as a topical anti-inflammatory for hemorrhoids, joint pain, ulcers and wounds (promotes tissue granulation).
- Used for anxiety, depression and sleep disturbances (220mg-400mg capsules 3 times/day)
- Can steep flowers in tea for 3-5 min. Comes in tinctures, oils, capsules.
- Safe in children. Avoid in early pregnancy due to smooth muscle relaxant. Large doses may interact with blood thinners.
5. Mastic Gum:
- Member of the pistachio tree family. Resin used in spices, gum, medicinal herbs.
- Has shown activity against H.pylori and used for duodenal ulcer healing.
- Take 350mg capsules 3 times/day for 3 weeks for heartburn and 500mg twice a day for 2 weeks for duodenal ulcers.
6. Turmeric:
- The anti-inflammatory properties of this herb is used in various conditions including peptic ulcer disease, Alzheimer’s, asthma and joint conditions to name just a few. The anti-inflammatory effects are equal to NSAIDs if dosed 1200-2000 mg/d. It’s absorption is increased if taken with black pepper extract.
- To treat peptic ulcer, recommended dose is 600mg capsule 5 times/day for 12 weeks. This would not include black pepper.
7. Cabbage Juice:
- Cabbage is in the cruciferous vegetable family (broccoli, cauliflower, Brussel sprouts, boy choy, etc) which are known for blocking carcinogens and detoxifying and is packed with vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.
- 1L cabbage fresh juice divided over the course of a day for 10 days has shown benefits for gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- Safe. Does contain vitamin K and can decrease effectiveness of Warfarin.
8. Iberogast®:
- This proprietary blend of 9 herbs (Clown’s mustard, German chamomile, angelica root, caraway, milk thistle, lemon balm, celandine, licorice root and peppermint leaf) has been studied and found to be effective for GERD related pain and nausea.
- 1 mL three times/day is well-tolerated,
- Side effects include nausea, diarrhea and skin rash
9. Glutamine:
- Amino acid that is used for cellular repair and new growth of the GI tract lining. Found in fish, eggs, chicken, beef, wheat, caggabe, beets, beans, spinach.
- Found to be effective for stress induced ulcers (studies done on burn victims).
- 400mg glutamine powder in water, 4 times/day is recommended.
- No side effects were reported.
10. Cranberry:
- Shown to not only impair E.coli from binding to bladder wall in the setting of UTI prevention but studies have also shown cranberry impairs adhesion of H. Pylori to gastric cell walls.
- 500 mL fresh cranberry juice or cranberry extract tablets 300-400 mg twice a day
11. Zinc/L-Carnosine (Poleprezinc):
- Chelated compound that is helpful with mucosal healing of the esophagus and gastric tissues.
- 37.5mg twice a day for 8 weeks. For every 15mg of Zinc, 1mg copper supplementation is recommended to prevent deficiency.
12. Vitamin C:
- Helps with eradication of H. Pylori.
- 1000 mg daily for anyone with active symptoms.
13. Probiotics:
- Lactobacillus and Saccharomyces have synergy with antibiotics for H. Pylori and can decrease the antibiotic-related side effects.
- Incorporating yogurt, aged cheeses, sauerkraut and other fermented vegetables into your diet on a regular basis can help prevent ulcer formation or recurrence.
Other Modalities to prevent ulcer formation and reduce pain
- Acupuncture
- Traditional Chinese Medicine (Chinese massage and herbs)
- Exercise – 1 study showed a 62% risk reduction for duodenal ulcers in men who walked over 10 miles/week.
- Stress reduction: yoga, tai chi, focused breathing, meditation
- Adequate sleep hygiene to maintain proper immune function
- Tobacco cessation – smoking increases ulcer formation rate by 4 times and reduces wound healing.
- Reducing alcohol intake. Red wine however has been shown to be protective against H. Pylori infection. Everything in moderation!
- Reducing NSAIDs due to its prostaglandin inhibition (prostaglandins are needed for mucosal protection of the GI tract).
References:
1. Rakel, D. (2018). Integrative Medicine (4th Edition). Philadelphia: Elsevier.
2. University of Arizona, Andrew Weil Center for Integrative Medicine Fellowship Modules. Lise Alchuler, ND. Botanical Foundations: GERD. 2019.
3. University of Wisconsin Integrative Medicine. An Integrative Approach to GERD. (Pearls for Clinicians). Online Handouts: Fammed.wisc.edu/integrative.
Other Articles by Dr. Ruby Rose, MD – Preparing for Flu Season.
———————————————————————————————————————-

Dr. Ruby Rose, MD, is board certified in emergency medicine. Originally from New York City, Dr. Rose graduated from Vassar College in New York before obtaining her medical degree from Tufts University School of Medicine in Boston, Massachusetts. She completed her emergency medicine residency at University of Massachusetts. Dr. Rose has a passion for alternative care and recently graduated from the University of Arizona Integrative Medicine Fellowship in Tucson, Arizona. After relocating to Texas with her family, Dr. Rose worked in St. David’s Healthcare System where she served in several leadership positions. In her spare time, she enjoys watching her kids play various sports and riding her horse in the Texas Hill Country.